Florida Supreme Court Backs DeSantis Redistricting Map

Florida Gov. Ron DeSantis’ push to redraw the state’s congressional map and give a substantial advantage to Republicans will likely remain in place for this year’s elections.
The state Supreme Court — in a 4-1 divided ruling in which two justices recused themselves — declined to wade into an ongoing legal dispute over the map. Voting and civil rights groups opposed to the GOP-approved redistricting map asked the state high court to block it in late May. They argue the redistricting maps violate Florida’s Fair Districts provisions, or anti-gerrymandering amendments in the state constitution.
The state Supreme Court’s decision means an appeals court will decide the current legal challenge.
The high court’s ruling comes just two weeks before candidates must qualify for this year’s elections, meaning that the legal challenge won’t be resolved in time for a different map to be in place for the 2022 elections. Florida’s primary will be held on Aug. 23.
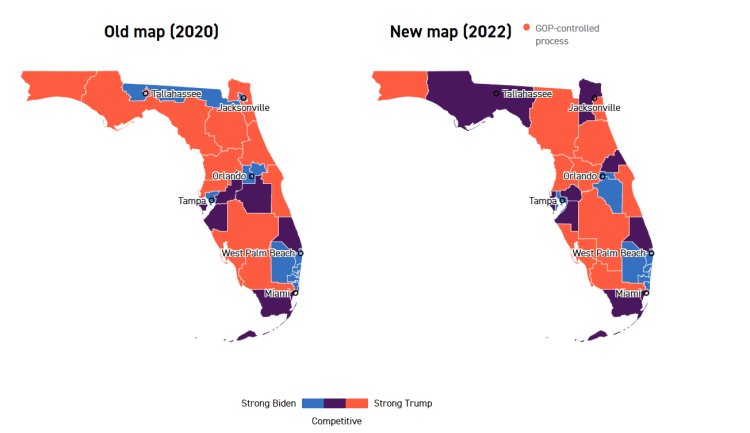
It also freezes in place for now a new congressional map for the nation’s third-largest state that will likely give Republicans a potential 20-8 advantage in a state where the GOP has only a slight voter registration advantage. This is another big blow to Democrats’ hopes of holding onto their majority in the U.S. House.
This new map also dismantles the North Florida congressional seat held by Rep. Al Lawson, a Black Democrat.
In its one-page decision, the Supreme Court contended it lacked “jurisdiction” over the current redistricting lawsuit and that it would be “speculative” to suggest “whether the First District’s eventual decision will provide an appropriate basis” for review. The decision was endorsed by four justices — including three who were appointed by DeSantis.
Passage of the new maps sparked the coalition of civil and voting rights groups to sue in state court to stop it from going forward.
Circuit Judge J. Layne Smith concluded the map proposed by DeSantis was likely unconstitutional because it violated the state’s Fair Districts standards because it diminished the clout of Black voters by redistributing them from Lawson’s seat into four districts.
Smith tried to impose a map that kept Lawson’s district intact, but that decision was upended by the 1st District Court of Appeal in May.

 Local News Staff
Local News Staff